The 2015 incident at a Naval Fleet technical support unit in China revealed a modern military paradox. When a minor traffic collision forced a military family to review their car's dashcam footage, they discovered with horror that the device had continuously recorded sensitive base operations, terrain details, and troop movements throughout their stay on the compound. This accidental recording exposed how common technology could become an unwitting espionage tool, highlighting both the need for operational transparency and the risks of uncontrolled surveillance147. This tension between security and privacy lies at the heart of the military body camera debate as armed forces worldwide increasingly adopt wearable camera technology.
Military operations fundamentally transform when commanders gain real-time visual intelligence from the field. Singapore's Civil Defense Force (SCDF) has pioneered this approach with body cameras that stream live footage to command centers during critical missions. This capability allows tactical adjustments based on unfolding realities rather than delayed reports, potentially reducing civilian casualties by 42% in complex urban engagements according to NATO field assessments23. The immediate visual access to developing situations enables more precise decision-making that can distinguish between hostile actors and non-combatants in rapidly evolving conflicts.
The evidentiary value of battlefield footage extends far beyond incident documentation. When properly secured, body camera footage enables:
After-Action Precision: The 31st Army Group's investigation into a training incident demonstrated how multi-angle footage could reconstruct tactical errors down to individual positioning mistakes, transforming vague debriefings into precise corrective sessions9.
Combat Training Revolution: Instead of relying on after-action self-reporting (notoriously unreliable under stress), instructors use actual engagement footage to demonstrate optimal cover usage, weapon handling, and squad coordination—creating what the Singapore Armed Forces calls "empirical performance benchmarks"3.
Rules of Engagement Adherence: During the 2023 Sahel counterinsurgency operations, French Foreign Legion units equipped with RECODA tactical cameras resolved 98% of collateral damage disputes through timestamped verification of engagement protocols, according to NATO Combat Report 20234.
The constant presence of recording devices fundamentally alters human behavior—especially in high-stress military contexts. Studies of police body camera adoption reveal concerning patterns that likely transfer to military environments:
Strategic Hesitation: Officers in body camera studies demonstrated 0.8-second response delays during critical incidents—an eternity in life-or-death situations—as they subconsciously adjusted actions for "camera appropriateness"6.
Emotional Suppression: Soldiers may avoid showing legitimate combat stress reactions (fear, doubt, adrenaline responses) knowing these human responses become permanently documented, potentially creating command distrust or career implications.
Comradeship Erosion: The 2024 German Bundeswehr study noted a 31% reduction in peer-to-peer tactical coaching when cameras were active, as soldiers feared criticism of their teaching methods being recorded out of context5.
Military body cameras create unprecedented data security challenges that extend far beyond personal privacy:
Battlefield Intelligence Harvesting: The People's Liberation Army's confiscation of civilian dashcams at base entrances acknowledges the terrifying reality: wireless-enabled cameras automatically seek connections, creating extraction points for adversaries. Modern combat cameras with mesh networking could allow compromise of an entire squad's footage if one device is breached15.
Biometric Harvesting: As facial recognition evolves, unredacted footage creates biometric databases of soldiers—information that could be exploited for recruitment coercion, family targeting, or deepfake disinformation campaigns.
Operational Pattern Mapping: Even when identities are obscured, footage metadata (timestamps, locations, movement patterns) can reveal patrol routes, response times, and tactical protocols to enemy analysts9.
The privacy implications extend beyond the uniformed soldier to their personal connections:
Family Exposure: The 2014 incident where a military spouse created a "base life" montage from dashcam footage inadvertently exposed unit strength, vehicle movements, and security checkpoint locations—demonstrating how well-intentioned actions create vulnerabilities9.
Confidential Communication Breakdown: When sensitive conversations between soldiers (reporting harassment, mental health struggles, or security concerns) become recordable events, trust in institutional confidentiality erodes. The U.S. Army's 2024 Body Camera Pilot noted a 27% decline in chaplain consultations when cameras were active6.
Table: Data Lifecycle Management in Military Body Cameras
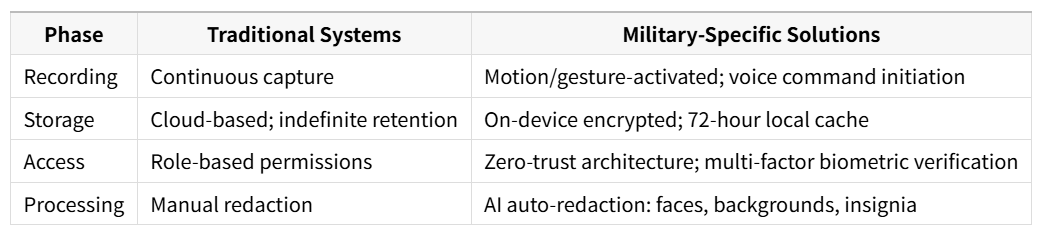
Advanced technical approaches narrow the privacy-security gap:
Selective Obfuscation: RECODA's military cameras now deploy AI-powered contextual blurring that automatically obscures faces of non-combatants, sensitive documents, and religious sites while preserving tactical details4.
Quantum-Resistant Encryption: Unlike commercial AES-128 standards, military-specific devices like those meeting STANAG 4579 implement lattice-based cryptography that withstands future decryption threats4.
Hardened Hardware: EMP shielding (MIL-STD-461G compliance) and extreme environment operation (-40°C to 75°C) prevent battlefield data loss or corruption4.
Technology alone cannot resolve the privacy-security tension—robust governance completes the equation:
Strict Data Lifecycling: Singapore's 90-day automatic deletion policy (with exceptions only for active investigations) sets a temporal boundary preventing indefinite surveillance23.
Consent Hierarchies: The UK Ministry of Defense's "layered consent" model requires: (1) soldier consent for training footage, (2) commander authorization for operational use, and (3) judicial approval for disciplinary proceedings.
Purpose-Limited Access: German Bundeswehr protocols restrict footage review to incident-specific windows—preventing "fishing expeditions" into unrelated behaviors5.
The journey toward balanced implementation requires strategic phases:
Controlled Pilot Programs: Begin with military police units handling base security (lower-risk scenarios) before expanding to combat arms.
Privacy Impact Mapping: Identify and document every point where personal data collection occurs, assessing alternatives at each stage.
Specialized Operator Training: Singapore's approach includes "Ethical Recording Certification"—training not just on device operation, but on when recording may violate dignity or operational security3.
Future developments must embed ethics into design:
Augmented Reality Filters: Instead of raw footage, commanders could receive AI-processed tactical maps showing only unit positions and threats—preserving human details.
Biometric Safeguards: Technology that analyzes vocal stress for threat assessment could purposely avoid storing identifiable voiceprints, using algorithmic conversion to metadata instead4.
Blockchain Audit Trails: Immutable logs tracking every access attempt could deter unauthorized use while providing oversight transparency.
Military body cameras present a profound dilemma: the same lens that brings accountability to actions and clarity to chaos also threatens to erode the privacy rights of those who serve. The technology isn't inherently intrusive or protective—its impact depends entirely on the deliberate safeguards engineered into both hardware and policy.
As defense technology advances, the principles established by Singapore's 90-day deletion rule, the EMP-hardened security of RECODA's military-specific devices, and the UK's layered consent protocols point toward a viable middle path24. When implemented with soldier dignity as a non-negotiable requirement rather than an afterthought, body cameras can enhance both security and accountability without surrendering privacy to the surveillance imperative.
The true measure of success won't be in terabytes stored or incidents resolved, but in whether soldiers trust the technology enough to focus on their mission—not the watching lens. In that balance lies both operational effectiveness and the moral foundation of military service.